-
May/June: What is Grade 3 studying?
ELA:
Module 4: Water Around the World
Module Summary: In this module, students deeply research and grow to understand the challenges and solutions other countries and cultures have in accessing fresh water. Students read One Well: The Story of Water on Earth by Rochelle Strauss throughout the module. The module intends not to show a single narrative about a country, geographic region, or ethnicity. Instead, the goal is for students to build their understanding of the importance of water for life and to help them recognize that people live in different ways in different places - there isn't only one way to do things.
Unit Tasks:
- Read an informational text and compare the main ideas and key details in the story One Well.
- Use information gathered from multiple sources to draft an opinion essay explaining why we should get involved in water conservation.
- In pairs, students create a PSA (public service announcement) about one of the three water issues studied earlier in the module: access to water, demands on water, and water pollution.
Eureka Math:
Module 7: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems
- Solve word problems, and share and critique peer solution strategies to varied word problems.
- Compare and classify quadrilaterals, as well as other polygons.
- Decompose quadrilaterals to understand perimeter as the boundary of a shape.
- Use all four operations to solve problems involving perimeter.
- Construct rectangles from a given number of unit squares and determine the perimeters.
-
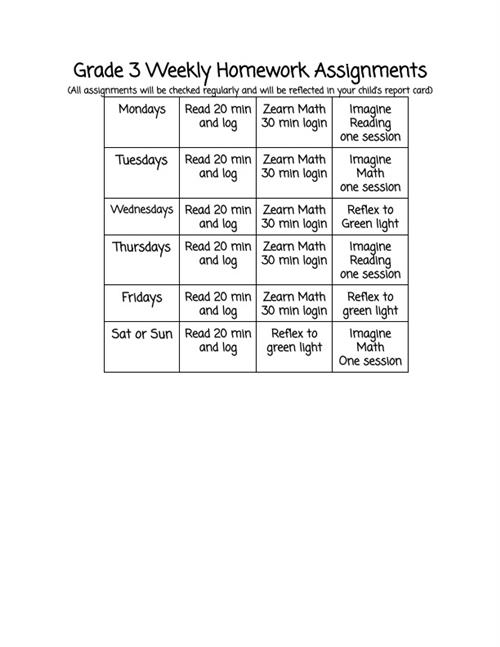
Grade 3 Homework, What to expect?
Homework is a crucial part of your child's active learning process and essential to their academic progress. Please make sure that all homework is completed daily.
- Remember, you are there to support your child's learning, but homework needs to be completed by your child.